It seems that the effects of cocaine use can be much more than pounding hearts, sweaty palms, and increased confidence.
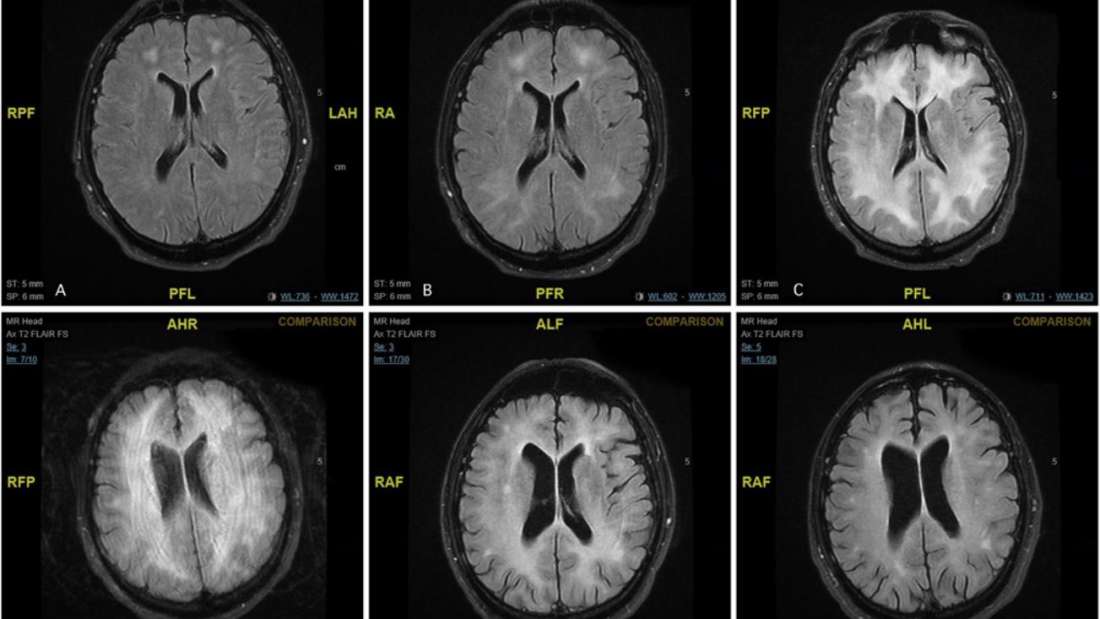
Doctors found after an MRI scan that cocaine literally eats away at your brain matter, leaving you confused and uncommunicative.
An MRI scan of the mans brain.
A case has reported that a 45 year old man showed up to the emergency room in Malta with confusion and unusual behaviour.
“The patient was not cooperative, unable to perform simple tasks and was not following commands,” Dr Ylenia Abdilla, the doctor who treated the man at Mater Dei Hospital in the Maltese city of Msida, said. “He was moving all four limbs in purposeful movement.”
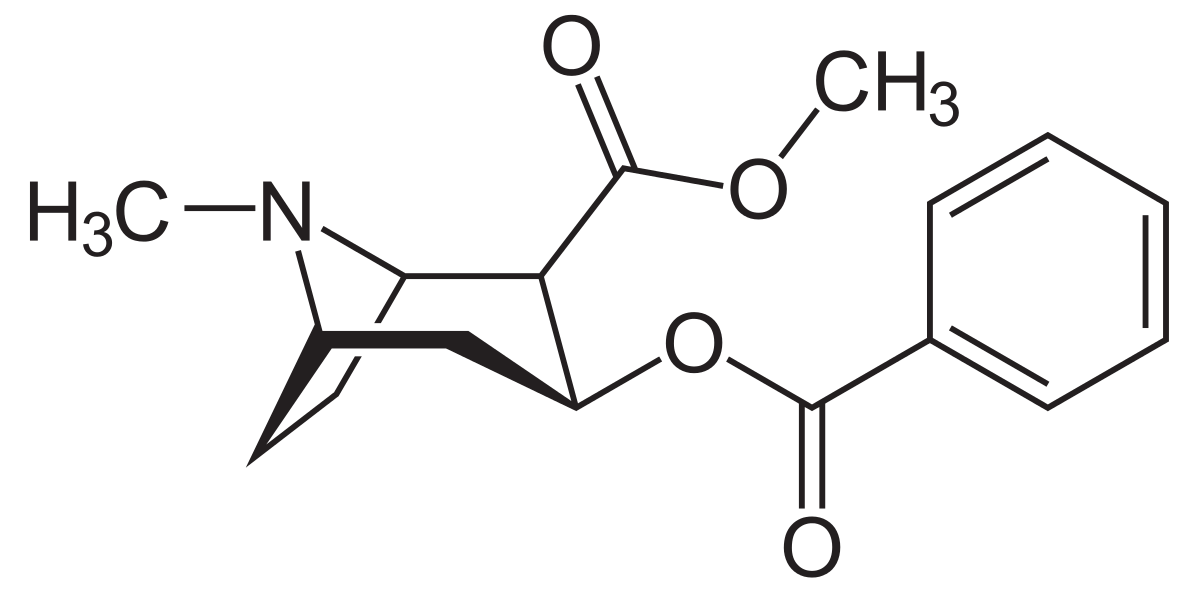
Chemical structure of cocaine.
The mans behaviour then took another turn for the worse when he became uncommunicative and eventually catatonic. Blood tests and other examinations were carried out and the results came back surprisingly normal, except for his white matter in his brain, it seemed to have been “eaten away”.
Doctors eventually diagnosed him with leucoencephalopathy, based on the scans. Leucoencephalopathy is the progressive damage or inflammation of the white matter of the brain. A similarly rare condition, known as progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, is known to be caused by an infection. But strangely enough, this patient shoewed no sign of infection.
They did discover quantities of cocaine in his urine after running a few more tests. Although the man hadn’t taken any drugs for two to three days, he admitted, and was clearly discovered to be, a regular cocaine user. Based on this, the doctors concluded that the mans mental deterioration was the result of cocaine abuse. It’s not exactly clear why cocaine causes this effect on the brain, but other studies have suggested that heavy drug use can result in splitting and unravelling of the layer that forms around nerves as well as swelling of the brain’s axons.
The man in question was treated using multiple drugs, and was independent and fully recovered a year later. He even checked into rehab to handle his addiction, and hasn’t done drugs for over a year now.
“He had not used drugs for 1 year. Apart from some complaints of low mood, he was fully independent and had returned to his previous functional status”.
To learn more on the effects of cocaine, or for help and support on anything drug related, click the link below.
https://www.talktofrank.com/drug/cocaine


